Jocko Hydrate vs LMNT: My Honest Comparison
Sodium governs extracellular fluid balance by controlling osmotic pressure and enabling active transport across intestinal and cellular membranes. The specific sodium salts used in hydration formulas shape how quickly they dissociate, how well they’re tolerated in the gut, and how they taste — all factors that influence real-world fluid intake under physical stress.
Jocko Hydrate and LMNT follow distinctly different formulation strategies. One pairs moderate sodium with functional compounds to support everyday training demands, while the other concentrates sodium density to match higher sweat losses. The contrast comes down to ingredient chemistry, not marketing positioning.
What Is Jocko Hydrate
Jocko Hydrate is a zero-sugar electrolyte drink built around moderate sodium levels with added compounds that support cognitive and metabolic function. Ingredients like L-theanine and D-ribose move it closer to a hybrid hydration-performance formula rather than a straightforward electrolyte replacement.
The product sits within the Jocko Fuel lineup, introduced in the early 2020s in the United States by former Navy SEAL Jocko Willink and his team. Development focused on creating a hydration option compatible with low-carb diets while avoiding artificial sweeteners common in traditional sports drinks.
Electrolyte concentrations are tuned for standard training sessions instead of extreme sweat conditions, keeping sodium lower to maintain drinkability during extended, casual use.
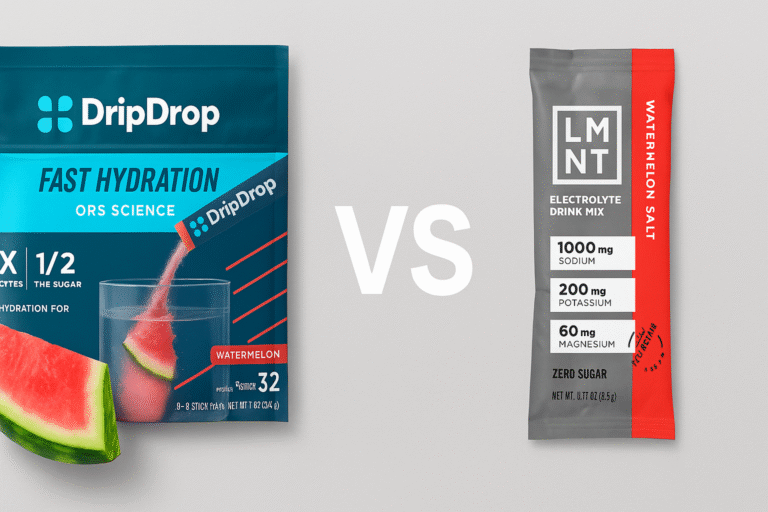
What Is LMNT
LMNT is a high-sodium electrolyte mix built on the premise that many athletes replace too little sodium relative to what they lose in sweat. The formula prioritizes sodium concentration and keeps the ingredient list intentionally minimal, avoiding additional functional compounds.
The company launched around 2019 under nutrition researcher Robb Wolf and collaborators after experimenting with higher sodium intake during low-carb dietary protocols. Its formulation reflects sweat composition research identifying sodium as the dominant electrolyte lost during prolonged exertion.
The product is designed for endurance training, heat exposure, and ketogenic diets where lower insulin levels increase sodium excretion through the kidneys.
Variety and Electrolyte Density
Jocko Hydrate comes in Lemon-Lime, Fruit Punch, Blue Raspberry, and Island Orange. A typical serving provides about 300 mg sodium and 200 mg potassium with zero sugar. Magnesium sits near 100 mg alongside vitamins B6 and B12, zinc, D-ribose, and L-theanine. These additions slightly increase osmolarity while expanding the formula’s functional scope beyond hydration alone.
LMNT flavors range from Citrus Salt and Orange Salt to Mango Chili and Chocolate varieties, plus an unsweetened option. Each stick delivers roughly 1000 mg sodium, 200 mg potassium, and 60 mg magnesium with zero sugar. The higher sodium concentration increases tonicity, supporting fluid retention during heavy sweat losses but creating a noticeably saltier taste profile.
Sweetener Systems
Jocko Hydrate relies exclusively on monk fruit extract. Mogrosides in monk fruit activate sweet taste receptors without triggering a glucose or insulin response, allowing sweetness without altering carbohydrate metabolism.
LMNT flavored varieties use stevia leaf extract, primarily rebaudioside A, to balance the strong salt presence. The raw version removes sweeteners entirely, catering to users who prefer no sweetness or are sensitive to stevia’s bitter notes.
These choices shape flavor perception: monk fruit delivers a softer sweetness curve, while stevia creates a sharper onset that complements high sodium intensity.
Sodium Chemistry
Jocko Hydrate
Sodium is supplied mainly as sodium chloride. Once dissolved, it separates into sodium and chloride ions absorbed through epithelial sodium channels and sodium-dependent transporters in the small intestine. The moderate concentration keeps osmolarity closer to plasma levels, lowering the chance of gastrointestinal discomfort during steady intake.
Additional sodium may appear within electrolyte blends paired with chloride, maintaining ionic balance without introducing buffering salts.
LMNT
LMNT sources most sodium from sodium chloride but also uses sodium citrate in certain flavors. Sodium citrate acts as a buffering agent that softens perceived saltiness and slightly raises solution alkalinity, improving palatability at higher sodium concentrations while supporting acid-base balance during prolonged exertion.
The elevated sodium load increases plasma osmolality more noticeably, encouraging water retention and reducing urine output during heavy sweating.
Functional Positioning
Jocko Hydrate suits scenarios where hydration is paired with mild cognitive support or moderate training sessions lasting a few hours or less. The inclusion of ribose, theanine, and vitamins shifts the product toward daily usability rather than targeted electrolyte replacement.
LMNT aligns with endurance athletes, training in hot environments, or ketogenic diets where renal sodium losses rise. The formulation assumes higher sodium turnover and prioritizes replacement efficiency over flavor neutrality.
Practical Decision Framework
Choose Jocko Hydrate when sodium needs remain moderate and added compounds like magnesium, ribose, and theanine align with daily training or general hydration habits. Its lower tonicity supports frequent intake without excessive salt exposure.
Choose LMNT when sweat sodium losses are substantial, workouts extend beyond standard gym sessions, or carbohydrate intake is low enough to increase sodium excretion. The higher sodium density allows smaller fluid volumes to maintain plasma volume more effectively.